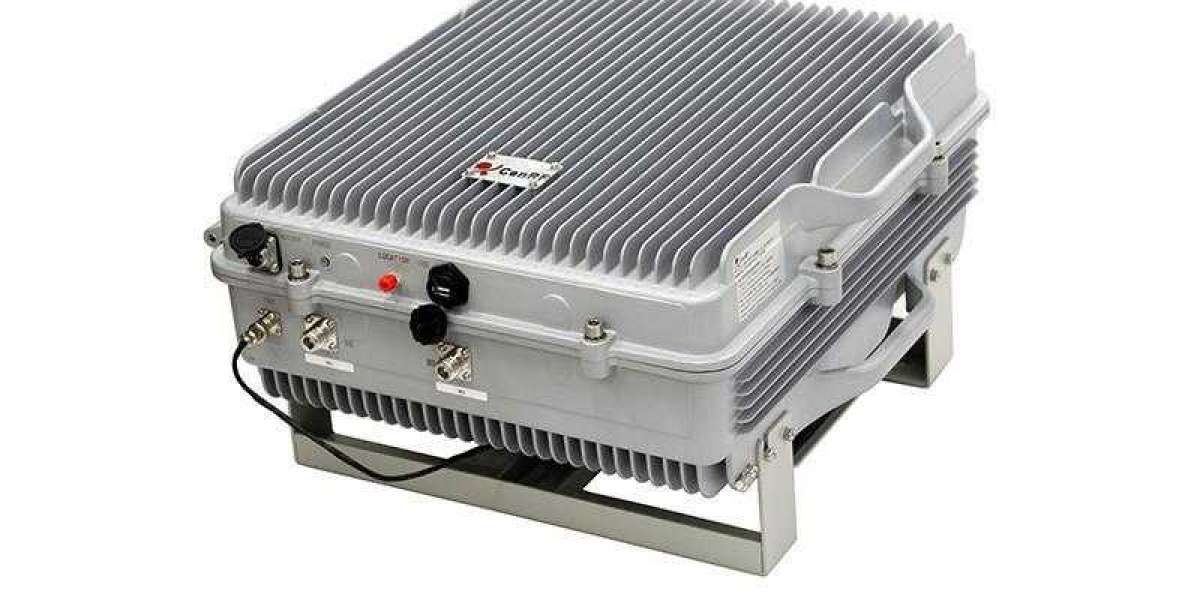
Repeaters are designed to give your network signals a boost so they can travel farther. So, how does a repeater work?
How the repeater works:
Due to the influence of the noise of the transmission line, the digital signal or analog signal carrying the information can only transmit a limited distance. The function of the repeater is to regenerate and transmit the received signal, thereby increasing the distance of the signal transmission. It connects two or more segments of the same network. For example, Ethernet often uses repeaters to expand the cable length of the bus. The length of each segment of standard thin-cable Ethernet is up to 185 meters, and there can be up to 5 segments. Therefore, after adding repeaters, the maximum network cable length can be increased to 925 meters. . In general, the part of the network at both ends of the repeater is a network segment, not a subnet.

The repeater can connect the cables of the two local area networks, retime and reproduce the digital signals on the cables, and then send them out. These functions are typical functions of the first layer in the OSI model - the physical layer. The function of the repeater is to increase the coverage area of the local area network. For example, the Ethernet standard stipulates that the maximum length of a single-segment signal transmission cable is 500 meters. up to 2500 meters. Some brands of repeaters can connect cable segments of different physical media, such as thin coaxial cable and fiber optic cable.
A repeater simply sends data on any cable segment to another cable segment, regardless of whether the data contains erroneous data or data that is not appropriate for the segment.
As a repeater manufacturer, CenRF specializes in manufacturing repeaters. If you are interested in repeaters, please pay attention to our website.